Iliopsoas syndrome
Iliopsoas bursitis / iliopsoas tendinitis
In iliopsoas syndrome, the bursa and/or tendon of the iliopsoas muscle are affected. This results in pain along the front of the hip, in the groin region. Iliopsoas syndrome often passes unrecognized as a cause of hip pain.
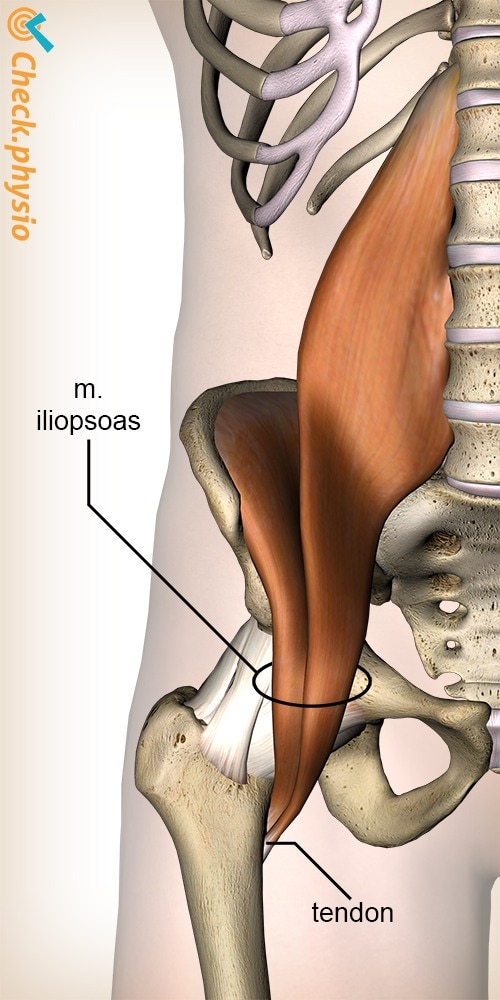
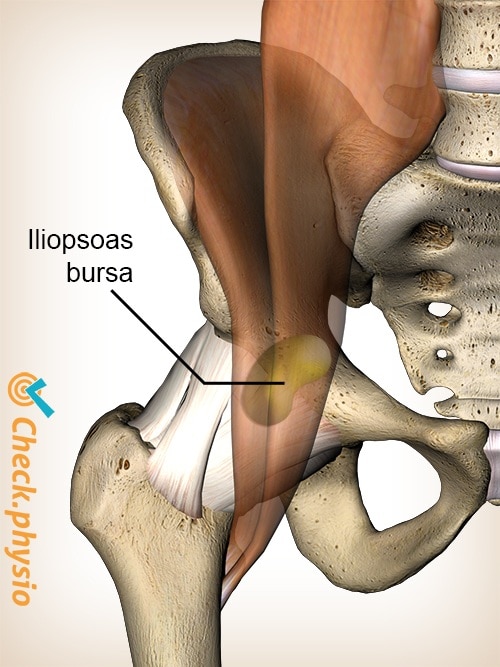
The iliopsoas is the muscle that flexes the hip joint and rotates the thigh outward. The iliopsoas attaches to the thigh bone (femur) through the tendon. The bursa located beneath the muscle ensures that everything slides smoothly and prevents friction. The bursa is approximately 5 to 7 cm long and 2 to 4 cm wide.
Description of condition
With iliopsoas syndrome, we are looking at bursitis or tendinitis. This means that the bursa or the tendon is inflamed. They may also be inflamed simultaneously. The presentation of symptoms of iliopsoas bursitis and iliopsoas tendinitis are virtually identical. This justifies the combination of these two conditions under the name iliopsoas syndrome.
Snapping hip
A snapping hip is often associated with iliopsoas syndrome. The tendon of the iliopsoas moves suddenly over a protruding bone ridge of the thigh or the pelvis. This is associated with a palpable (and sometimes audible) "snap". If the structures are inflamed, the snapping hip causes pain at the moment of "snapping".
Cause and history
The 3 most important causes of iliopsoas bursitis are acute trauma, overloading or rheumatoid arthritis. The symptoms can occur as a result of lifting heavy objects with the hip extended, running (uphill), rowing, athletics and strength training. It is common in athletic individuals.
Signs & symptoms
- Pain in the groin region, along the front of the hip.
- A (painful) snapping can often be felt in the hip.
- Maximum bending of the hip can be painful.
- Pain is felt during activities such as: standing up from a seated position, putting on shoes or socks, walking up a hill or steps, running and kicking.
- The pain may sometimes radiate along the front of the thigh to the knee.
- The symptoms decrease when at rest.
- The stride length of the affected side may be shorter when walking, because the patient tries to avoid a painful extension of the hip.
Diagnosis
Treatment
The treatment consists of an exercise program for the iliopsoas muscle. Strength training and stretching exercises play an important role in this and should be increased gradually and carefully. A physiotherapist can assist with this.
If the symptoms do not go away, a corticosteroid injection can be considered. In exceptional cases surgery can be performed, although success cannot be guaranteed.
Exercises
A professional exercise programme has been compiled with exercises for iliopsoas syndrome.
You can check your symptoms using the online physiotherapy check or make an appointment with a physiotherapy practice in your locality.
References
Johnston, C.A., Wiley, J.P., Lindsay, D.M. & Wiseman, D.A. (1998). Iliopsoas bursitis and tendinitis. A review. Sports Med. 1998 Apr; 25(4):271-283.
Verhaar, J.A.N. & Linden, A.J. van der (2005). Orthopedie. Houten: Bohn Stafleu van Loghum.



